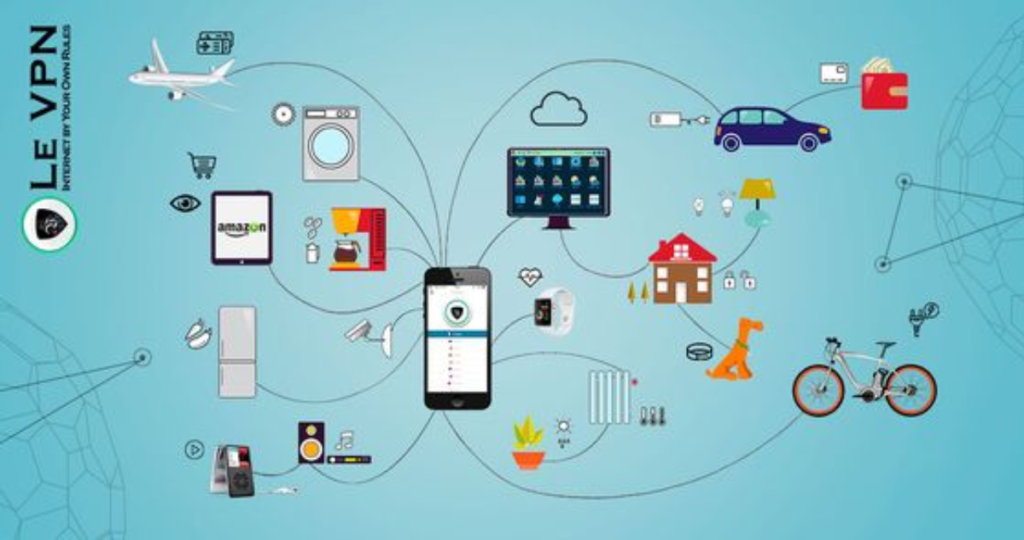
Hey there! Welcome to our ultimate guide to the Internet of Things (IoT). If you’re reading this, chances are you’re curious about the buzz surrounding IoT and want to learn more. Well, you’re in the right place! In this guide, we’ll take you on a journey to explore the world of IoT, its applications, benefits, challenges, and what the future holds.
It’s changing how we interact with devices, machines, and each other. In 2024, understanding IoT is crucial for businesses, individuals, and societies to stay ahead of the curve. IoT is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a reality that’s transforming industries and shaping our daily lives.
In this guide, we’ll demystify IoT, explore its history, and dive into the key concepts and terminology. We’ll also delve into the applications, benefits, and challenges of IoT, as well as its future implications. By the end of this journey, you’ll be equipped with a solid understanding of IoT and its potential to transform your life and business.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices, also known as “smart devices,” can collect and share data, enabling them to interact with the physical world and with each other.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Before we dive deeper into IoT, let’s get familiar with some key concepts and terminology:
- Devices: Physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, such as smart thermostats or wearable fitness trackers.
- Sensors: Components that detect and measure physical parameters, like temperature or motion.
IoT Applications and Use Cases
IoT is transforming various aspects of our lives, from industries to daily routines. Let’s explore some exciting applications and use cases:
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Predictive Maintenance: IIoT sensors monitor equipment performance, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Quality Control: IIoT devices track production lines, ensuring consistency and quality.
Consumer IoT (CIoT)
- Smart Homes: CIoT devices control lighting, temperature, and security, making homes more comfortable and secure.
- Wearables: CIoT wearables track fitness, health, and wellness, empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
- Smart Appliances: CIoT-enabled appliances optimize energy consumption and simplify household chores.
IoT Technology and Protocols
Devices and Sensors
- Sensors: Temperature, motion, light, and sound sensors detect and measure physical parameters.
- Actuators: Devices that perform actions based on sensor data, such as adjusting temperature or lighting.
Connectivity Options
- Wi-Fi: Wireless connectivity for devices in close proximity.
- Bluetooth: Low-power, short-range connectivity for devices.
- 5G: High-speed, low-latency connectivity for mission-critical applications.
Benefits and Advantages of IoT
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation: IoT devices automate tasks, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity.
- Optimization: IoT data analytics optimize processes, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Improved Decision-Making and Automation
- Data-Driven Insights: IoT data provides actionable insights for informed decision-making.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: IoT devices make decisions based on real-time data.
Challenges and Concerns of IoT
While IoT offers numerous benefits, it also raises several concerns:
Security and Privacy Risks
- Hacking: IoT devices are vulnerable to hacking, compromising personal data and privacy.
- Data Breaches: Unsecured data storage and transmission lead to data breaches.
Data Management and Integration
- Data Overload: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, making management and analysis challenging.
- Integration: Integrating IoT data with existing systems and infrastructure can be complex.
IoT Security and Privacy
Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Unsecured Devices: Unpatched vulnerabilities in IoT devices leave them open to attacks.
- Weak Passwords: Weak passwords and authentication mechanisms compromise IoT security.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices and Data
- Regular Updates: Regularly update IoT devices with security patches and firmware updates.
- Encryption: Encrypt IoT data both in transit and at rest.
- Secure Authentication: Implement robust authentication mechanisms.
Future of IoT
Emerging Trends and Technologies
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered IoT devices will enhance decision-making and automation.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology will ensure secure and transparent IoT data management.
Predictions and Forecasts for IoT Growth and Adoption
- Increased Adoption: IoT adoption will increase across industries, driving growth and innovation.
- Market Size: The global IoT market is expected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2027.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, our ultimate guide to the Internet of Things (IoT) has taken us on a journey through the vast landscape of connected devices, exploring the what, why, and how of this revolutionary technology. We’ve delved into the applications and use cases, technologies and protocols, benefits and advantages, challenges and concerns, security and privacy measures, and future trends and predictions. From industrial automation to smart homes, healthcare to transportation, and artificial intelligence to blockchain, we’ve seen how IoT is transforming industries and aspects of our lives. As we embrace this interconnected world, let us remember that the true power of IoT lies not in the devices, but in the connections they foster – between people, machines, and the world around us. So, let us harness this power to create a brighter, more efficient, and more compassionate future, where technology serves humanity, and the Internet of Things becomes the Internet of Life.